The UCLA California Policy Lab (CPL) recently released a new analysis of California unemployment insurance (UI) claims as part of a policy briefs series publishing research conducted in partnership with the Labor Market Information Division of the California Employment Development Department.
Overview
Historically, the share of unemployed workers receiving regular UI benefits (recipiency rate) in California has been relatively low (as has also been the case in other states). This Data Point combines administrative data from California’s Employment Development Department (EDD) with monthly Current Population Survey (CPS) data to construct an improved recipiency rate to measure the extent to which unemployed and underemployed Californians are receiving regular UI benefits.
Dr. Till von Wachter, a co-author of the analysis, UCLA economics professor and faculty director at the California Policy Lab, says about this new analysis, “The share of unemployed workers receiving UI benefits tends to rise during economic downturns, but even during the Great Recession, we didn’t approach the high rates that we’re seeing now.”
Three key findings from this new research:
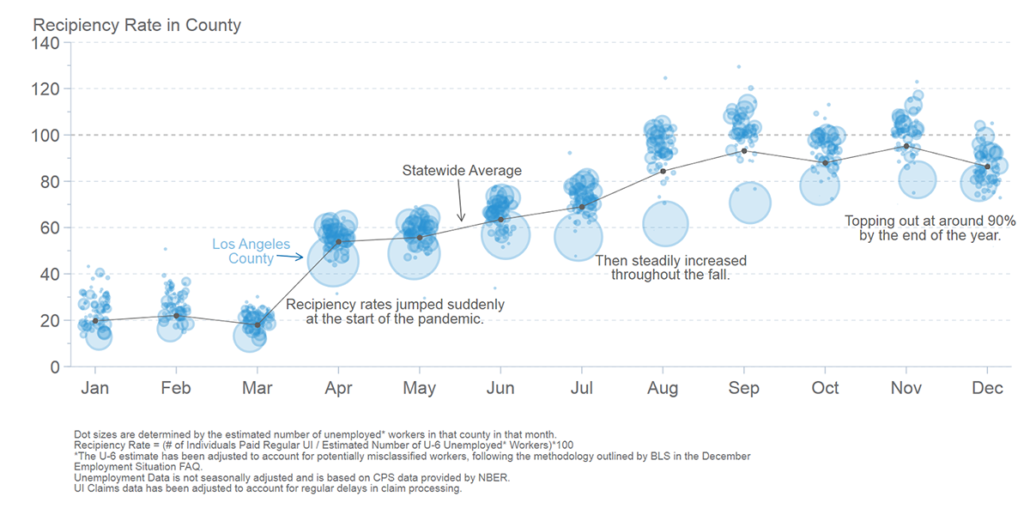
1) The recipiency rate in California has increased dramatically over the course of the crisis, from about 50% in April to nearly 90% in December.
The analysis found that over 2.5 million unemployed Californians were not receiving regular UI benefits in April and May 2020, and while some of these workers likely received benefits under the Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) program, at least 500,000 workers did not. As the share of workers receiving regular UI benefits increased, the number of workers not receiving regular UI benefits decreased, hovering at around 250,000 in the last four months of 2020.
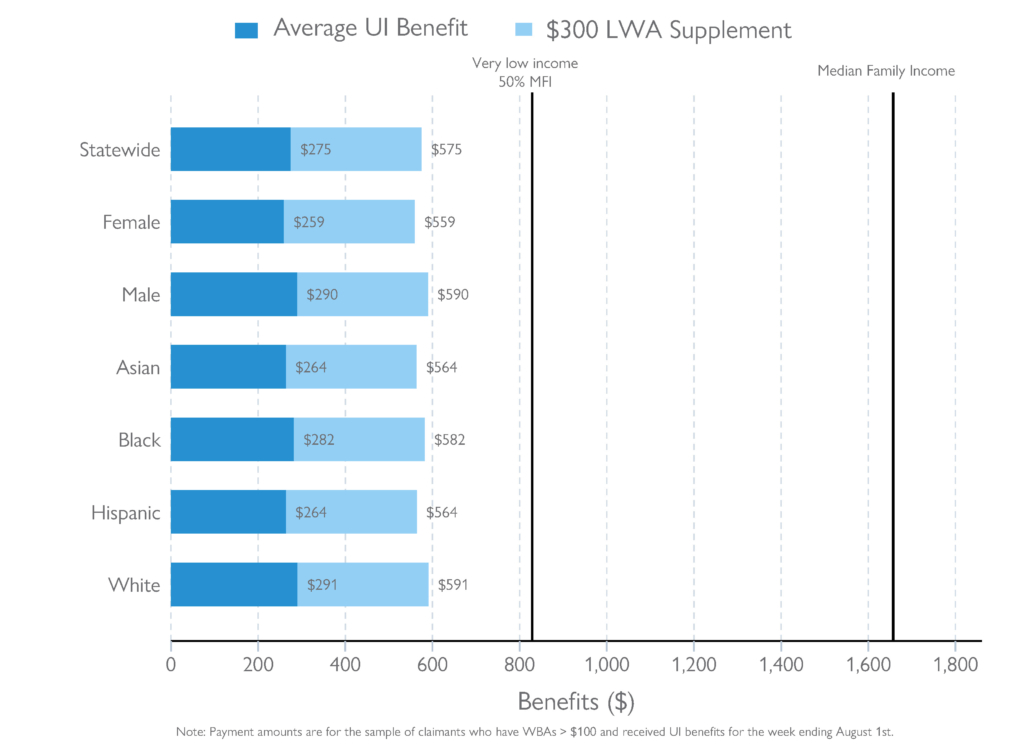
2) There are geographic disparities in the rates of UI benefit collection that correlate with income, race and ethnicity, access to technology, and other social and economic factors. In counties with higher median household incomes, a larger share of their unemployed workers tended to receive UI benefits, while a smaller share of unemployed workers received benefits in counties with higher poverty rates.
3) CPL’s Recovery Index highlights substantial county-level differences in the economic recovery. Higher-income counties have recovered more quickly than lower-income counties, while counties with a higher share of Black and Hispanic residents have seen slower recoveries than counties with more White residents.
To see the map which tracks the Labor Market Recovery, click HERE.
To see table code of County Level Measures of Economic Recovery and UI Recipient Rates, click HERE.
To read CPL’s latest policy brief on this issue, click HERE.







 As an economist and director of the
As an economist and director of the 